Lab (Week 1) — Introduction to Pipetting and Dilutions


Overview
Objective
Welcome to HTGAA! This is our very first lab, and in this lab we will introduce students to the foundational techniques of pipetting and serial dilutions, critical for precise liquid handling and solution preparation in biological and chemical experiments.
This is a one-day lab with two protocols covered on mixing colors and dilution. By the end of the lab, students will confidently use pipettes, prepare solutions with desired concentrations, and troubleshoot common errors in pipetting.
Concepts Learned & Skills Gained
Students will:
- Understand Units and Conversions: moles (mol), molarity (M), and conversions between µL, mL, and L.
- Perform Serial Dilutions: Learn the stepwise dilution process to achieve specific solution concentrations.
- Gain Pipetting Proficiency: Operate P20, P200, and P1000 pipettes accurately for volume transfers.
- Visualize Mixing Outcomes: Use colors and absorbance measurements to observe concentration gradients.
Pre-Lab
Reading
Key Definitions
Here are some key definitions we’d like you to know before you get started.
- Moles (mol): A unit representing $6.022 \times 10^{23}$ particles (atoms, molecules, etc.).
- Molarity (M): Concentration defined as moles of solute per liter of solution (mol/L).
- Conversions:
- 1 L = 1000 mL = 1,000,000 μL 1 M = 1000 mM = 1,000,000 μM
Planning Your Experiments
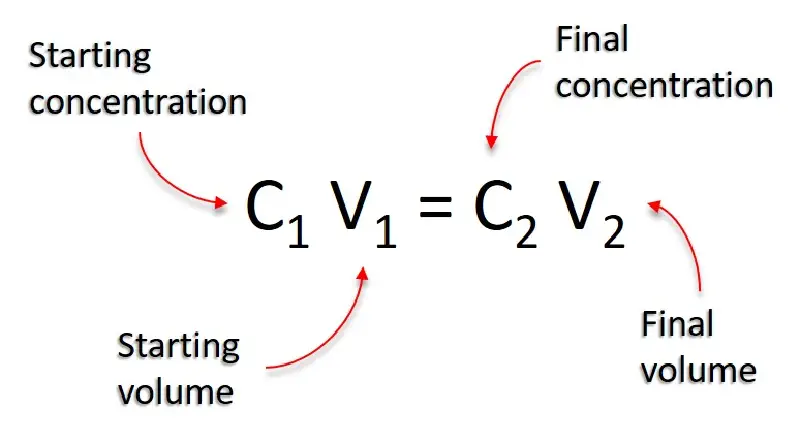

To calculate the volume of water needed for a dilution, use the formula: $$C_1 V_1 = C_2 V_2$$
Where:
- $C_1$ : Initial concentration (stock concentration).
- $V_1$ : Volume of stock solution needed.
- $C_2$ : Final concentration (desired concentration).
- $V_2$ : Final volume (total volume of the diluted solution).
Steps:
Rearrange the formula to calculate $V_1$: $$ V_1 = \frac{C_2 V_2}{C_1} $$
Calculate the volume of water (let’s call it $V_Water$) to add: $$ V_Water = V_2 - V_1 $$
Practice
Dilution Practice 1
- Scenario: The stock concentration of a mystery substance (MS) is 5 M. Calculate how to dilute to 100 µM (0.1 mM):
- Use sequential 1:499 and 1:99 dilution steps for accurate preparation.
- Step 1: Dilute 5 M (5,000,000 µM) to 10,000 µM (500x dilution).
- Step 2: Dilute 10,000 µM to 100 µM (100x dilution).
- Use sequential 1:499 and 1:99 dilution steps for accurate preparation.
Dilution Practice 2
- The stock concentration of a mystery substance (MS) is 5 M.
- If the molar mass of MS is 532 g/mol, what’s the concentration of the stock concentration in g/mL? To make your life easier, you can use one of many online calculators.
- You will perform a serial dilution to get 100 uM of MS. Devise a plan to dilute a 5 M MS solution to 100 uM. How many dilution steps will we need? Which tubes should we use? Which pipettes?
- Fill out the following chart to prepare a final reaction with 60 uL reaction volume. Why did we make 100 uM MS if we actually need 40 uM MS? Why not prepare 40 uM in serial dilutions?
| Reagent | Stock concentration | Desired concentration | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loading dye | 6X | 1X | |
| MS | 100 uM | 40 uM | |
| dH2O | n/a | n/a |
Note
Please fill this out before coming to lab.
Additional resources
You must watch or be able to understand the following videos:
- https://thecrashcourse.com/courses/unit-conversion-significant-figures-crash-course-chemistry-2/
- Dilution Problems, Chemistry, Molarity & Concentration Examples, Formula & Equations
Protocol
Overview
Materials
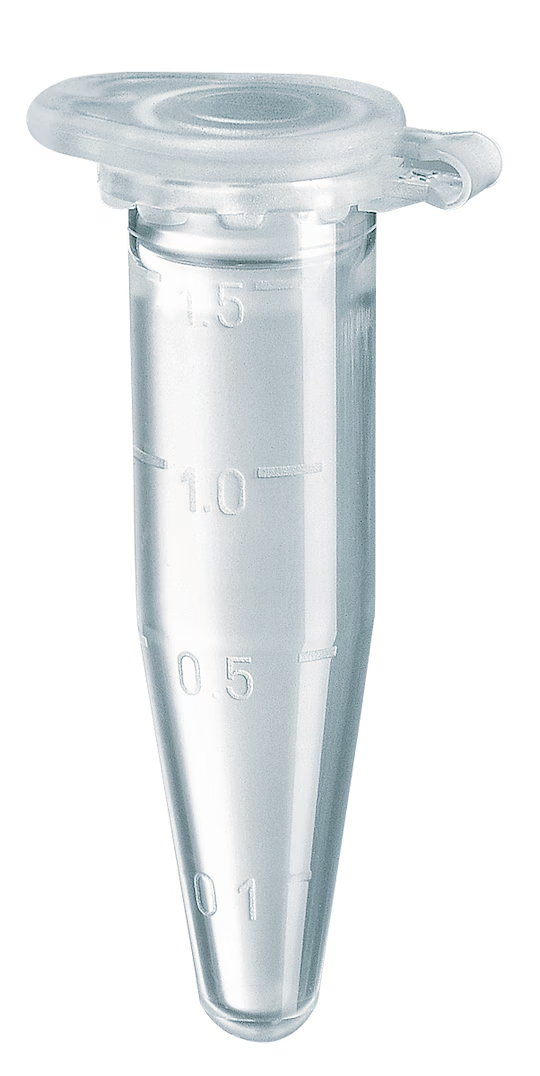

Eppendorf Tube
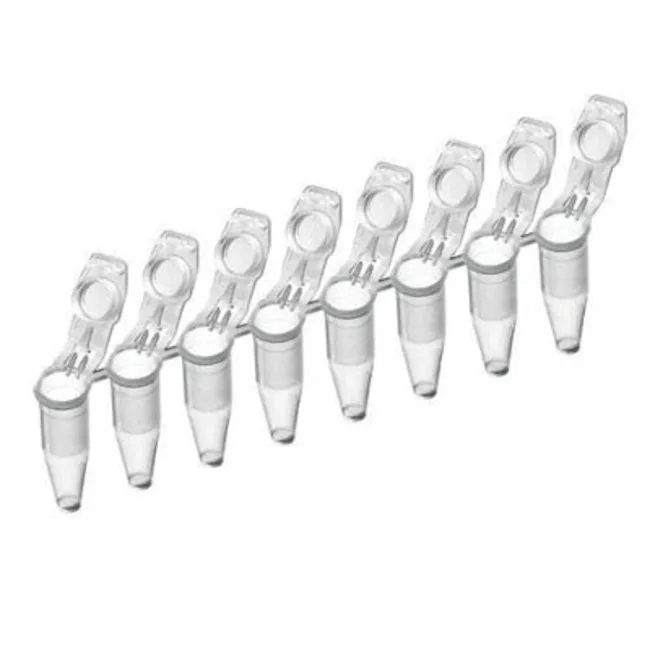

PCR Tube Strip
- Pipettes
- P20: 1-20uL of liquid
- P200: 20-200uL
- P1000: 100-1000uL
- Pipette tips: 10uL, 200uL, 1000uL
- Tubes
- Eppendorf tube (see image)
- PCR tubes: (see image)
- Tube holder
- Stock reagents
- dH2O
- Mysterious substance (food coloring with water), henceforth: MS
- Red, Blue and Yellow food coloring solutions
- Gel loading dye (commonly used reagents for loading gels, strong purple color)
Part 1: Mixing Color
- Prepare tubes with red, yellow, and blue food coloring solutions OR watercolor
- Take ten tubes and mark them with numbers 1 to 6
- Tube 1, 2 and 3: add 500 uL each red, yellow, and blue solution to the tube.
- Tube 4: add 220 uL red solution to the tube, and add 220 uL yellow solution.
- Try adding this in 2 steps: add 200 uL first, and then 20 uL. Discard your tips after you add one color!
- Tube 5: add 525 uL yellow solution to the tube, and add 525 uL blue solution.
- Tube 6: add 155 uL red solution to the tube, and add 155 uL blue solution. Now you have a rainbow! You can try mixing other colors with the solutions.
- Try plating different volumes (e.g. 1uL, 2uL, 5uL, 10uL) on a petri plate to make some designs and build your intuitive understanding of these volumes.
Part 2: Performing Serial Dilution
- Perform serial dilutions to get 100 uM (0.1 mM) of MS.
- Every time you mix in liquid, pipette up and down three or four times to ensure the two liquids are mixed thoroughly.
- Mark each tube with its respective concentration using a pen.
- Prepare a final reaction of 60 uL based on your table in the pre-lab.
- Bonus: Take 20 uL from the final reaction and pipette it to a pre-prepared gel well. Wells are a bit trickier because they are thin and your pipette tip will puncture the gel if you’re not careful. Be gentle!